Using FastPro
In this chapter we will learn about Using the FastPro extension.
This extension is added to the Ring language starting from Ring 1.19.
Contents:
Bytes2List() function
List2Bytes() function
UpdateList() function
UpdateColumn() function
UpdateBytesColumn() function
AddBytesColumn() function
Bytes2List() function
Syntax:
Bytes2List(cBytes,nWidth,nHeight,nChannels) —> aList // [[R,G,B],…]
List2Bytes() function
Syntax:
List2Bytes(aList,nChannels) —> cBytes // “RGBA….”
UpdateList() function
A function that could update 1D and 2D lists and provide very high performance.
This function support using numbers only.
Syntax:
updateList(<aList>,<cCommand>,<cSelection>,<nPara1>,[<nPara2>],[nPara3])
cCommand could be :set, :add, :sub, :mul, :div, :merge and :copy
cSelection could be :col, :row, :manycols, :manyrows and :items
Example:
updateList(<aList>,:set,:row,<nRow>,<nValue>)
updateList(<aList>,:set,:col,<nCol>,<nValue>)
updateList(<aList>,:set,:manyrows,<nRowStart>,<nRowEnd>,<nValue>)
updateList(<aList>,:set,:manycols,<nColStart>,<nColEnd>,<nValue>)
updateList(<aList>,:set,:items,<nValue>)
updateList(<aList>,:copy,:row,<nRowSrc>,<nRowDest>)
updateList(<aList>,:copy,:col,<nColSrc>,<nColDest>)
updateList(<aList>,:merge,:row,<nRowDest>,<nRow>)
updateList(<aList>,:merge,:col,<nColDest>,<nCol>)
updateList(<aList>,:mul,:col,<nCol>,<nValue>,<nColDest>)
The required parameters depend on the cCommand/cSelection.
The parameters could be columns/rows numbers.
Also, some commands requires a value like the set command.
Example:
load "fastpro.ring"
aList = [ [1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
7:9 ]
# Set the values of the first row to 10
updateList(aList,:set,:row,1,10)
# Add 10 to each value in the first row
updateList(aList,:add,:row,1,10)
# Sub 5 from each value in the first row
updateList(aList,:sub,:row,1,5)
# Multiply each value in the first row by 10
updateList(aList,:mul,:row,1,10)
# Divide each value in the first row by 2
updateList(aList,:div,:row,1,2)
# Copy the first row values to the second row
updateList(aList,:copy,:row,1,2)
# Sum the third row and the second row
# And the result will be in the third row
updateList(aList,:merge,:row,3,2)
? aList
Output:
The list will be [ [75,75,75], [75,75,75], [82,83,84] ]
75
75
75
75
75
75
82
83
84
Using :col as the third parameter we can do operations on the list columns.
Example:
load "fastpro.ring"
# Store [ [1,2,3], [4,5,6], [7,8,9] ] in aList
aList = [ 1:3,
4:6,
7:9 ]
updateList(aList,:set,:col,1,100)
updateList(aList,:mul,:col,2,10)
updateList(aList,:div,:col,3,3)
? aList
Output:
The list will be [ [100,20,1], [100,50,2], [100,80,3] ]
100
20
1
100
50
2
100
80
3
We can determine a destination column through the six parameter.
Example:
load "fastpro.ring"
aList = [
[10,20,0],
[30,40,0],
[50,60,0]
]
updateList(aList,:mul,:col,1,10,3)
? aList
Output:
The list will be [ [10,20,100], [30,40,300], [50,60,500] ]
10
20
100
30
40
300
50
60
500
Using :manyrows or :manycols we can do operations on many rows/columns
Example:
load "fastpro.ring"
aList = [
1:3,
4:6,
7:9
]
# Starting from row 1 to row 2, set each value to 100
updateList(aList,:set,:manyrows,1,2,100)
# Starting from row 2 to row 3, multiply each value by 10
updateList(aList,:mul,:manyrows,2,3,10)
? aList
Output:
100
100
100
1000
1000
1000
70
80
90
Using :items as the third parameter we can do operations on 1D lists.
Example:
load "fastpro.ring"
aList = 1:5
updateList(aList,:set,:items,1000)
updateList(aList,:mul,:items,2)
? aList
Output:
The list will be [2000,2000,2000,2000,2000]
2000
2000
2000
2000
2000
UpdateColumn() function
Syntax:
updateColumn(<aList>, [<cCommand>,<nPara1>,[<nPara2>],[nPara3]],…)
Using this function we can execute many commands on the list columns.
Instead of using updateList() many times and each time we pass :col as the third parameter, we can use updateColumn().
This function support using numbers only.
Note
The ImagePixel application uses a similar function called updateBytesColumn() to process bytes directly.
Generate Image
The next example generate an image using a string that contain bytes
Then uses Bytes2List() to convert the generated image to Ring List
Using updateColumn() the list is updated and the colors are converted to Gray
Then using List2Bytes() we get another string contains bytes that represent the Gray Image
Then using the drawBytes() method in RingQt - QPainter class we draw the generated images
Note
We can update the string bytes directly without conversion to a Ring list
Tip
It’s better to use the updateBytesColumn() function to reduce memory usage and have better performance
load "stbimage.ring"
load "fastpro.ring"
load "lightguilib.ring"
width = 640
height = 480
channels = 3
cImage = space(width*height*channels)
RVALUE = 1
GVALUE = 2
BVALUE = 3
WindowWidth = Width*2 + 100
nIndex=0
for x=1 to height
for y=1 to width
cImage[nIndex++] = x*x
cImage[nIndex++] = x*y
cImage[nIndex++] = x*2
next
next
aList = Bytes2List(cImage,Width,Height,Channels,255)
updateColumn(aList,:mul,RVALUE,0.3, # R *= 0.3
:mul,GVALUE,0.59, # G *= 0.59
:mul,BVALUE,0.11, # B *= 0.11
:merge,RVALUE,GVALUE, # R += G
:merge,RVALUE,BVALUE, # R += B
:copy,RVALUE,GVALUE, # G = R
:copy,RVALUE,BVALUE) # B = R
cGrayImage = list2Bytes(aList,Channels,255)
MyApp = new QApp
{
win1 = new QWidget()
{
setwindowtitle("Generate Image & Convert it to Gray")
setgeometry(0,0,WindowWidth,Height)
Canvas = new QLabel(win1)
{
MonaLisa = new QPixMap2( WindowWidth, Height)
daVinci = new QPainter()
{
begin(MonaLisa)
drawbytes(0,0,cImage,width,Height,channels)
drawbytes(width+10,0,cGrayImage,width,Height,channels)
endpaint()
}
setPixMap(MonaLisa)
}
show()
}
exec()
}
Output:
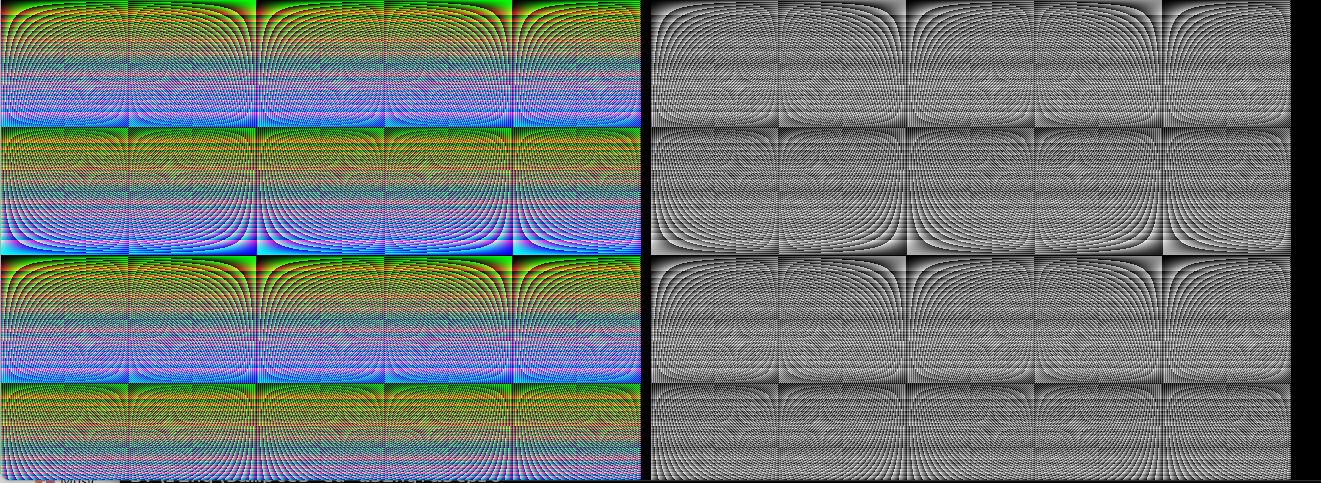
A faster version of the previous sample could be written by replacing the next code
aList = Bytes2List(cImage,Width,Height,Channels,255)
updateColumn(aList,:mul,RVALUE,0.3, # R *= 0.3
:mul,GVALUE,0.59, # G *= 0.59
:mul,BVALUE,0.11, # B *= 0.11
:merge,RVALUE,GVALUE, # R += G
:merge,RVALUE,BVALUE, # R += B
:copy,RVALUE,GVALUE, # G = R
:copy,RVALUE,BVALUE) # B = R
cGrayImage = list2Bytes(aList,Channels,255)
With this code
cGrayImage = updateBytesColumn(cImage,Channels,Width*Height,255,
:mul,RVALUE,0.3, # R *= 0.3
:mul,GVALUE,0.59, # G *= 0.59
:mul,BVALUE,0.11, # B *= 0.11
:merge,RVALUE,GVALUE, # R += G
:merge,RVALUE,BVALUE, # R += B
:copy,RVALUE,GVALUE, # G = R
:copy,RVALUE,BVALUE) # B = R
UpdateBytesColumn() function
Using this function we can process the Bytes directly instead of using Bytes2List() & List2Bytes()
Syntax:
updateBytesColumn(cBytes, nColumns, nCount, nDiv, [cCommand,nPara1,nPara2,[nPara3]],…) —> cNewBytes
Example:
load "stbimage.ring"
load "fastpro.ring"
RVALUE = 1
GVALUE = 2
BVALUE = 3
CIMAGE = "ring.jpg"
# Image Information
width=0 height=0 channels=0
# Ring will Free cData automatically in the end of the program
? "Load image: " + CIMAGE
cData = stbi_load(CIMAGE,:width,:height,:channels,STBI_rgb)
# Convert to Gray
cNewData = updateBytesColumn(cData,channels,width*height,255,
:mul,RVALUE,0.3, # R *= 0.3
:mul,GVALUE,0.59, # G *= 0.59
:mul,BVALUE,0.11, # B *= 0.11
:merge,RVALUE,GVALUE, # R += G
:merge,RVALUE,BVALUE, # R += B
:copy,RVALUE,GVALUE, # G = R
:copy,RVALUE,BVALUE) # B = R
# Write the image
? "Writing mynewimage.bmp"
stbi_write_bmp("mynewimage.bmp", width, height, channels, cNewData)
system("mynewimage.bmp")
This function is used in the ImagePixel application to convert the image to Gray.
AddBytesColumn() function
If we have an image that uses three channels (R,G,B) and is represented through a string of bytes
We can use AddBytesColumn() function to add an extra channel like the Alpha channel.
Syntax:
addBytesColumn(cBytes, nColumns, nCount) —> cNewBytes
Example:
cImageFile = "ring.jpg"
nImageWidth = 0
nImageHeight = 0
nImageChannels = 0
stbi_info(cImageFile,:nImageWidth,:nImageHeight,:nImageChannels)
if nImageChannels = 3
cImageData = stbi_load(cImageFile,:nImageWidth,:nImageHeight,:nImageChannels,STBI_rgb)
cImageData = addBytesColumn(cImageData,nImageChannels,nImageWidth*nImageHeight)
nImageChannels = 4
else
cImageData = stbi_load(cImageFile,:nImageWidth,:nImageHeight,:nImageChannels,STBI_rgb_alpha)
ok