Building RingQt Applications for Mobile¶
In this chapter we will learn about Building RingQt Applications for Mobile.
Download Requirements¶
Check the next link : http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/androidgs.html
Download
The Android SDK Tools
The Android NDK
Apache Ant v1.8 or later
Java SE Development Kit (JDK) v6 or later
Update the Android SDK¶
Update the Android SDK to get the API and tools packages required for development
Install Qt for Android¶
You can install Qt for Android from the next link
- Run Qt Creator, Select Tools > Options > Android to add the
Android NDK and SDK paths.
Using Qt Creator Open the project
Folder : ring/android/ringqt/project
Project file : project.pro
You will find the code in resourcestest.ring
You can modify the code then build and run for Desktop or Mobile.
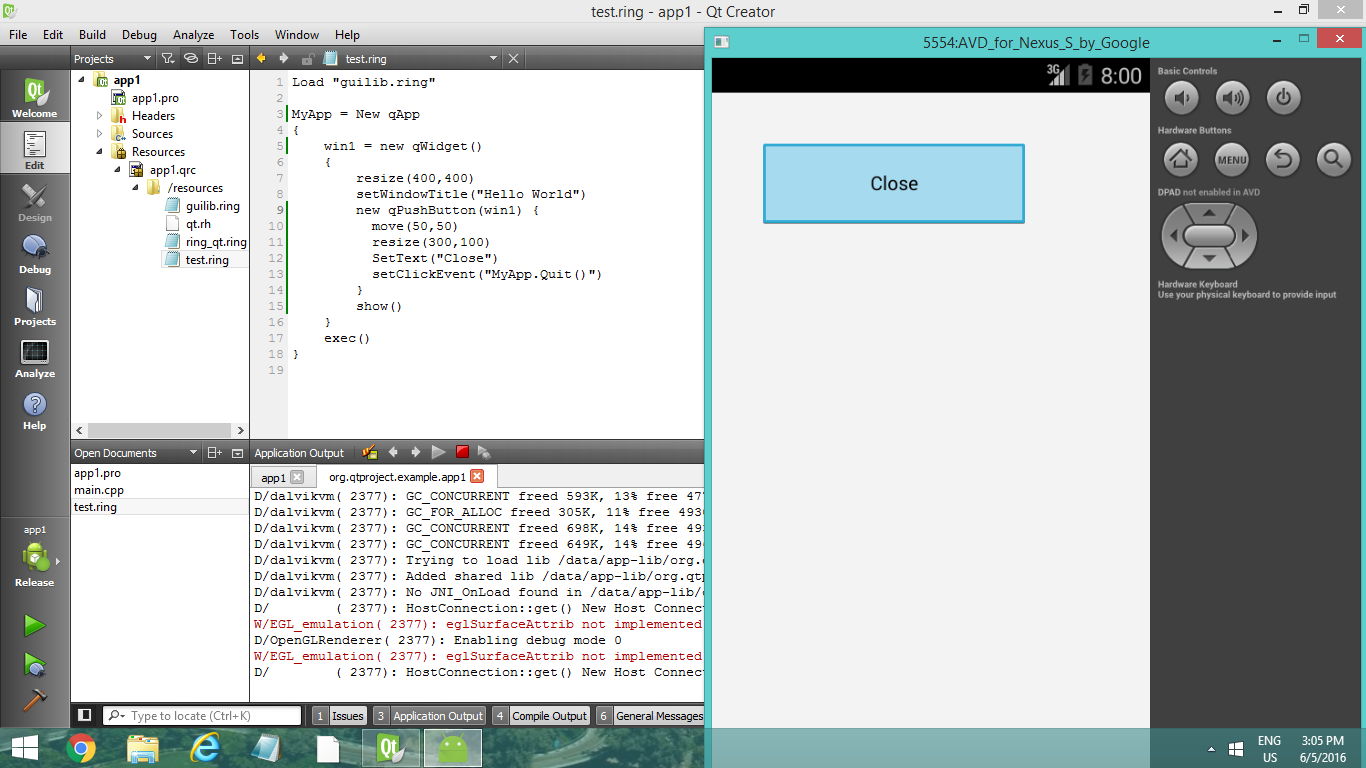
Comments about developing for Android using RingQt¶
The main project file is main.cpp
This file load Ring Compiler/Virtual Machine and RingQt
Then copy files during the runtime from the resources to temp. folder
Then run the test.ring
Through main.cpp you can extract more files from the resources to temp. folder once you add them (create projects with many files).
The next functions are missing from this Ring edition
- Database (ODBC, SQLite & MySQL)
- Security and Internet functions (LibCurl & OpenSSL)
- RingAllegro (Allegro Library)
- RingLibSDL (LibSDL Library)
Just use Qt Classes through RingQt.
For database access use the QSqlDatabase Class
Note
All of the missing libraries ((LibCurl, OpenSSL & Allegro) can be compiled for Android, but they are not included in this Qt project.
- use if isandroid() when you want to modify the code just for android
Example:
if isandroid()
// Android code
else
// other platforms
ok
(4) Sometimes you will find that the button text/image is repeated in drawing ! it’s Qt problem that you can avoid using the next code.
if isandroid()
setStyleSheet("
border-style: outset;
border-width: 2px;
border-radius: 4px;
border-color: black;
padding: 6px;")
ok
- Always use Layouts instead of manual setting of controls position and size.
This is the best way to get the expected user interface to avoid problems like (controls with small/extra size)
- When you deal with Qt Classes you can determine the images from resources (you don’t need to copy them using main.cpp)
Example:
if isandroid()
mypic = new QPixmap(":/resources/cardsimage")
else
mypic = new QPixmap("cards.jpg")
ok
In the previous example, cards.jpg is added to the resources then we write the “cardsimage” as alias for “cards.jpg”