Object Oriented Programming (OOP)
In this chapter we are going to learn how to use the Object-Oriented programming paradigm inside the Ring programming language.
We will learn about
Classes and Objects
Access Objects Using Braces
Composition
Setter and Getter
Private Attributes and Methods
Operator Overloading
Inheritance
Dynamic Attributes
Packages
Printing Objects
Find() and List of Objects
Sort() and List of Objects
Using Self.Attribute and Self.Method()
Using This.Attribute and This.Method()
Command: New From
Classes and Objects
We can define new classes using the next syntax
Syntax:
Class <Class Name> [From|<|: <Parent Class Name>]
[Attributes]
[Methods]
[Private
[Attributes]
[Methods]
]
And we can create objects using the next syntax
Syntax:
New <Object Name> [ (init method parameters) ] |
[ { access object data and methods } ] ---> Object
Example:
New point { x=10 y=20 z=30 print() }
Class Point x y z func print see x + nl + y + nl + z + nl
Note
We can use { } to access object data and methods.
Tip
we can declare the class attributes directly after the class name.
Output:
10
20
30
We can rewrite the same program in another style
New point # create new object using the point class
{ # access the new object attributes and methods
x = 10 # set the x attribute to 10
y = 20 # set the y attribute to 20
z = 30 # set the z attribute to 30
print() # call the print method
} # end of object access
Class Point # define the Point class
x y z # the class contains three attributes x, y & z
func print # define the print method
see x + nl + # print the x attribute
y + nl + # print the y attribute
z + nl # print the z attribute
Also we can write the same program in another way
P1 = New Point
P1.x = 10
P1.y = 20
P1.z = 30
P1.Print()
Class Point x y z func print see x + nl + y + nl + z + nl
Note
we can use the dot operator after the object name to access object members.
Also we can write the same program in another way
new point { print() }
Class Point
x = 10 y = 20 z = 30
func print see x + nl + y + nl + z + nl
Note
we can set the default values for the class attributes when we declare them.
Also we can write the same program in another way
new point(10,20,30)
Class Point
x y z
func init p1,p2,p3 x=p1 y=p2 z=p3 print()
func print see x + nl + y + nl + z + nl
Note
we can call the init method directly using () when we create new objects
Also we can write the same program in another way
new point( [ :x = 10 , :y = 20 , :z = 30 ] )
Class Point x y z
func init aPara x = aPara[:x] y = aPara[:y] z = aPara[:z] print()
func print see x + nl + y + nl + z + nl
Tip
using Hash for passing method parameters enable us to create optional parameters and change the order of parameters when adding them to the Hash.
Access Objects Using Braces
We can access the object at any time using braces { }
Inside the braces we can use the object attributes and methods directly
This can be done when we create the object using the New keyword or at any time using the next syntax
ObjectName { access object data and methods }
Example:
See "Creating the Object" + nl
o1 = new Point
See "Using the Object" + nl
o1 {
x=5
y=15
z=25
print()
}
Class Point x y z func print see x + nl + y + nl + z
We can use braces to access objects when we call functions or methods
Example:
o1 = new Point
print( o1 { x=10 y=20 z=30 } )
func print object
see object.x + nl +
object.y + nl +
object.z
Class Point x y z
We can mix between using braces and the dot operator to access the object in the same expression.
Example:
o1 = new Point
O1 { x=10 y=20 z=30 }.print()
Class Point x y z
func print see x + nl + y + nl + z
Composition
The object may contains other objects as attributes.
Using braces to access objects can be nested.
Example:
R1 = New Rectangle
{
Name = "Rectangle 1"
P1
{
X = 10
Y = 20
}
P2
{
X = 200
Y = 300
}
Color = "Blue"
}
see "Name : " + R1.Name + nl +
"Color: " + R1.Color + nl +
"P1 : (" + R1.P1.X + "," + R1.P1.Y + ")" + nl +
"P2 : (" + R1.P2.X + "," + R1.P2.Y + ")"
Class Rectangle
name color
p1 = new Point
p2 = new Point
Class Point x y
Output:
Name : Rectangle 1
Color: Blue
P1 : (10,20)
P2 : (200,300)
Setter and Getter
We can define methods to be used when we set and get object attributes.
Syntax:
Class ClassName
AttributeName
...
Func SetAttributeName
...
Func GetAttributeName
...
Example:
o1 = new person
o1.name = "Mahmoud" see o1.name + nl
o1 { name = "Ahmed" see name }
Class Person
name family = "Fayed"
func setname value
see "Message from SetName() Function!" + nl
name = value + " " + family
func getname
see "Message from GetName() Function!" + nl
return "Mr. " + name
Output:
Message from SetName() Function!
Message from GetName() Function!
Mr. Mahmoud Fayed
Message from SetName() Function!
Message from GetName() Function!
Mr. Ahmed Fayed
Private Attributes and Methods
We can define private attributes and methods after the keyword private inside the class body
Note
A subclass could access private attributes/methods defined in the parent class.
Tip
Once we create an object, no other object (even from the same class) could access it’s private attributes/methods directly.
Example:
o1 = new person {
name = "Test"
age = 20
print()
o1.printsalary()
}
try
see o1.salary
catch
see cCatchError + nl
done
try
o1.increasesalary(1000)
catch
see cCatchError + nl
done
Class Person
name age
func print
see "Name : " + name + nl +
"Age : " + age + nl
func printsalary
see "Salary : " + salary + nl
private
salary = 15000
func increasesalary x
salary += x
Output:
Name : Test
Age : 20
Salary : 15000
Error (R27) : Using private attribute from outside the class : salary
Error (R26) : Calling private method from outside the class : increasesalary
Operator Overloading
We can add the operator method to our class to enable using operators with the class objects.
Syntax:
Class ClassName
...
Func operator cOperator,Para
...
The function operator takes two parameters, the first represent the operator and the second represent the second parameter after the operator.
Example:
o1 = new point { x = 10 y = 10 print("P1 : ") }
o2 = new point { x = 20 y = 40 print("P2 : ") }
o3 = o1 + o2
o3.print("P1+P2 : ")
class point x y
func operator cOperator,Para
result = new point
switch cOperator
on "+"
result.x = x + Para.x
result.y = y + Para.y
on "-"
result.x = x - Para.x
result.y = y - Para.y
off
return result
func print cPoint
see cPoint + "X : " + x + " Y : " + y + nl
Output:
P1 : X : 10 Y : 10
P2 : X : 20 Y : 40
P1+P2 : X : 30 Y : 50
The next example from the List class in the stdlib.ring
Func operator cOperator,Para
result = new list
switch cOperator
on "+"
if isobject(para)
for t in Para.vValue
vValue + t
next
but islist(para)
for t in Para
vValue + t
next
ok
on "len"
return len( vValue )
on "[]"
return &vValue[para]
off
return result
The “len” operator is used with (for in) control structure.
The “[]” operator is used when we try to access the list items, In this case we use the & operator to return the item values like strings and numbers by reference, so we can update it when we access the items.
Another Example
func main
See "----1"+nl
a1 = new BigNumber( "123" )
a2 = new BigNumber( "456" )
a3 = new BigNumber( "789" )
See nl+"----2"+nl
a1.print()
a2.print()
a3.print()
See nl+"----3"+nl
a2 = a1 + "45"
See nl+"----4"+nl
a2.print()
See nl+"----5"+nl
a3 = a1 + a2
See nl+"----6"+nl
a3.print()
See nl+"----7"+nl
###==================================
Func FuncAdd( num1, num2)
Sum = 0 + num1 + num2 ### Para.aData isNumber
Sum = "" +Sum ### Para.adata isString
return Sum ### return to Class
###===================================
class BigNumber
### Variables
aData = "468"
### Functions INIT default values
func init aPara
? "INIT aPara: " ? aPara
if isString(aPara)
aData = aPara
else
aData = "" + aPara
ok
### Other Functions
func operator cOperator, Para
whatType = Type(Para)
? nl+"WhatType-PARA: "+ whatType ? Para
? nl+"Operator: " ? cOperator ? nl+"PARA: " ? Para ? " ______" ? nl
if whatType = "STRING"
dataInfo = Para
? "dataInfo String: " ? dataInfo
but whatType = "NUMBER"
datinfo = "" + Para
? "dataInfo Number: " ? dataInfo
else whatType = "OBJECT"
dataInfo = "" + para.aData
? "dataInfo OBJECT: " ? dataInfo
ok
? "dataInfo USING: " ? dataInfo
### Para.aData does NOT exist on first pass ( Object with member)
### Result isObject when assigned "self"
result = self
switch cOperator
on "+"
answer = FuncAdd( aData, dataInfo )
? nl+"AnswerString - FunAdd aData, dataInfo: " ? answer
### result = self, is Object, populate Object with aData member
result.aData = answer
off
### Result = Self is Object
return result
func print
? nl+"ClassPrint aData: " ? aData
Inheritance
We can create class from another class in the class definition using the keyword from.
Syntax:
Class <Class Name> [From <Parent Class Name>]
We can call a method in the parent class from the child class using Super.
Note
Super provide access to the methods only (No access to the attributes).
Tip
Using ParentClassName(self) we can know the parent class name or get an empty string if no parent class exists.
Syntax:
func methodname
...
super.methodname()
...
Example:
Func main
e1 = new Employee {
Name = "test"
age = 20
job = "programmer"
salary = 20000000
print()
}
Class Human
Name Age
func print
see "Name : " + name + nl + "Age : " + age + nl
Class Employee from Human
Job Salary
func print
super.print()
see "Job : " + job + nl + "Salary : " + salary + nl
Output:
Name : test
Age : 20
Job : programmer
Salary : 20000000
Dynamic Attributes
We can write instructions after the class name to be executed when we create new objects
Example:
o1 = new dynamicClass
see o1.var5 + nl # output 5
Class DynamicClass
for x = 1 to 10
cStr = "var" + x + " = " + x
eval(cStr)
next
Tip
in the previous example var1, var2, …, var10 will be defined as attributes.
Tip
The problem with the previous example is that x and cStr will be defined as attributes too!
Note
we can write class definitions inside a string then using eval() we can execute the string to define the classes
Packages
We can create a package (a group of classes under a common name) using the next syntax
package PackageName
Class Class1
...
Class Class2
...
Class Class3
...
...
Example
o1 = new System.output.console
o1.print("Hello World")
Package System.Output
Class Console
Func Print cText
see cText + nl
Note
we can use the dot operator as part of the package name
Instead of typing the long name PackageName.ClassName we can use the import command
When we import a package, we can use any class inside this package directly.
Example
import system.output
o1 = new console {
print("Hello World")
}
Package System.Output
Class Console
Func Print cText
see cText + nl
Printing Objects
We can print the object state (attributes and values) using the see command.
Example:
see new point { x=10 y=20 z=30 }
class point x y z
Output:
x: 10.000000
y: 20.000000
z: 30.000000
Find() and List of Objects
We can use the find() function to search inside a list of objects.
Syntax:
Find(List,ItemValue,nColumn,cAttribute) ---> Item Index
Example:
myList1 = [new Company {position=3 name="Mahmoud" symbol="MHD"},
new Company {position=2 name="Bert" symbol="BRT"},
new Company {position=1 name="Ring" symbol="RNG"}
]
see find(mylist1,"Bert",1,"name") + nl
see find(mylist1,"Ring",1,"name") + nl
see find(mylist1,"Mahmoud",1,"name") + nl
see find(mylist1,"RNG",1,"symbol") + nl
see find(mylist1,"MHD",1,"symbol") + nl
see find(mylist1,"BRT",1,"symbol") + nl
see find(mylist1,3,1,"position") + nl
see find(mylist1,1,1,"position") + nl
see "Other" + nl
see find(mylist1,"test",1,"name") + nl
see find(mylist1,"test",0,"name") + nl
see find(mylist1,"test",5,"name") + nl
class company position name symbol
Output:
2
3
1
3
1
2
1
3
Other
0
0
0
Sort() and List of Objects
We can sort a list of objects based on an object attribute using the Sort() function.
Syntax:
Sort(List,nColumn,cAttribute) ---> Sorted List based on Object Attribute
Example:
myList1 = [
new Company {position=3 name="Mahmoud" symbol="MHD"},
new Company {position=2 name="Bert" symbol="BRT"},
new Company {position=8 name="Charlie" symbol="CHR"},
new Company {position=6 name="Easy" symbol="FEAS"},
new Company {position=7 name="Fox" symbol="EFOX"},
new Company {position=5 name="Dog" symbol="GDOG"},
new Company {position=4 name="George" symbol="DGRG"},
new Company {position=1 name="Ring" symbol="RNG"}
]
see sort(mylist1,1,"name")
see copy("*",70) + nl
see sort(mylist1,1,"symbol")
see copy("*",70) + nl
see sort(mylist1,1,"position")
class company position name symbol
Output:
position: 2.000000
name: Bert
symbol: BRT
position: 8.000000
name: Charlie
symbol: CHR
position: 5.000000
name: Dog
symbol: GDOG
position: 6.000000
name: Easy
symbol: FEAS
position: 7.000000
name: Fox
symbol: EFOX
position: 4.000000
name: George
symbol: DGRG
position: 3.000000
name: Mahmoud
symbol: MHD
position: 1.000000
name: Ring
symbol: RNG
**********************************************************************
position: 2.000000
name: Bert
symbol: BRT
position: 8.000000
name: Charlie
symbol: CHR
position: 4.000000
name: George
symbol: DGRG
position: 7.000000
name: Fox
symbol: EFOX
position: 6.000000
name: Easy
symbol: FEAS
position: 5.000000
name: Dog
symbol: GDOG
position: 3.000000
name: Mahmoud
symbol: MHD
position: 1.000000
name: Ring
symbol: RNG
**********************************************************************
position: 1.000000
name: Ring
symbol: RNG
position: 2.000000
name: Bert
symbol: BRT
position: 3.000000
name: Mahmoud
symbol: MHD
position: 4.000000
name: George
symbol: DGRG
position: 5.000000
name: Dog
symbol: GDOG
position: 6.000000
name: Easy
symbol: FEAS
position: 7.000000
name: Fox
symbol: EFOX
position: 8.000000
name: Charlie
symbol: CHR
Using Self.Attribute and Self.Method()
Inside the class region (After the class name and before any method) and the class methods we can use self.attribute and self.method()
Class Point
self.x = 10
self.y = 20
self.z = 30
func print
see self.x + nl + self.y + nl + self.z + nl
Note
using self.attribute in the class region to define the class attribute protect the class attributes from conflict with global variables.
Tip
if we defined the class attributes without using self or this and there are a global variable with the same name it will be used and the attribute will not be defined.
Check the “Scope Rules” chapter to know about the conflict between the global variable name and the attribute name
What this may happens?
Because
Because in the class region we can access global variables.
Before defining any variable, Ring try to find the variable and use it if it’s found.
Note
Try to avoid the global variables, use the main function and start their names with $
Tip
In large programs protect your classes and define their members using self.attribute
Tip
A better solution to avoid using self and this in the class region is to use different global scope and the load package command
Using This.Attribute and This.Method()
Inside class methods we have access to the object scope directly. we don’t need to use Self.attribute or Self.method to read/write attribute and call methods.
But we can use braces {} while we are inside methods to access another object, In this case the current object scope will be changed while we are inside the brace.
How we can get access to our class attributes and methods while we are inside braces?
This can be done using This.Attribute and This.Method()
Example:
new point
class point
x=10 y=20 z=30
print()
func print
new UI {
display(this.x,this.y,this.z)
}
Class UI
func display x,y,z
see x + nl + y + nl + z + nl
Using This in the class region as Self
The class region is the region that comes after the class name and before any method.
We can use This in the class region as Self.
Example:
func main
o1 = new program {
test()
}
? o1
class program
this.name = "My Application"
this.version = "1.0"
? name ? version
func test
? "Name = " + name
? "Version = " + version
Output
My Application
1.0
Name = My Application
Version = 1.0
name: My Application
version: 1.0
Note
When we use braces to change the current active object, Using This we can still point to the class.
Tip
The difference between This and Self is that Self point to the current active object that we can change using braces.
Remember that in most cases we don’t need to use This or Self in the class region
We can write
class program name version
Or
class program name="My Application" version="1.0"
Note
We use This or Self in the class region just to avoid conflict with global variables that are defined with the same name.
Default value for object attributes
The default value for object attributes is NULL
In Ring, the NULL value is just an empty string or a string that contains “NULL”
We can check for NULL values using the isNULL() function
Example:
oProgram = new Program
? oProgram.name
? oProgram.version
? isNULL(oProgram.name)
? isNULL(oProgram.version)
oProgram { name="My Application" version="1.0" }
? isNULL(oProgram.name)
? isNULL(oProgram.version)
? oProgram
class program
name
version
Output:
NULL
NULL
1
1
0
0
name: My Application
version: 1.0
Command: New From
Using (new) we can create a new object from a specific class
Using (new from) we provide a variable which contains the class name
Example:
cClassName = "myclass2"
myobj = new from cClassName
cClassName = "myclass"
myobj = new from cClassName
class myclass
? :hello
class myclass2
? :wow
Output:
wow
hello
Using Objects During Definition
Starting from Ring 1.19, The language provides better support for using objects during definition where we can mix between this feature and other features like operator overloading without missing the output
Example:
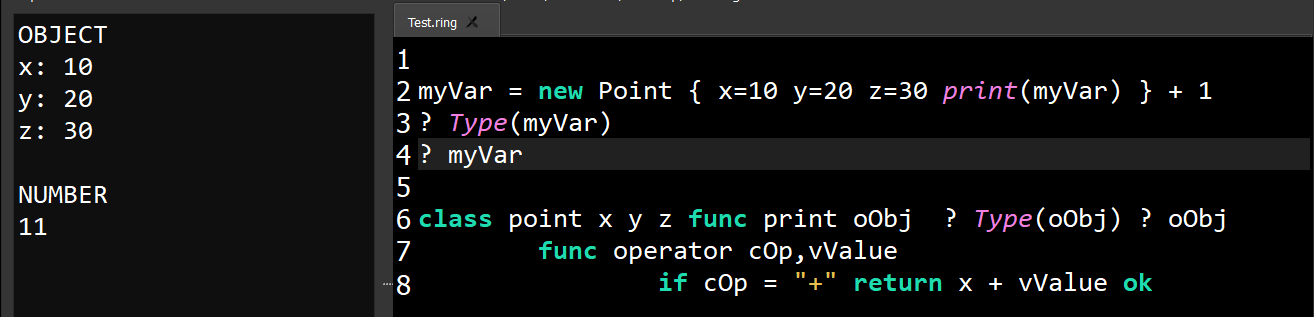
The new point object will be stored directly in myVar during definition
We can pass myVar as parameter to the print() method
Using + 1 will call the operator() method
The operator() method output will be stored in myVar
This means that the Assignment operation is executed TWO TIMES!
The first Assignment is executed to support (Using objects during definition) where myVar is an object contains the new point while in the second time, the Assignment is executed to support storing the Operator Overloading output.
Note
RingQt samples uses this feature to quickly pass the parent window object to the other widgets.